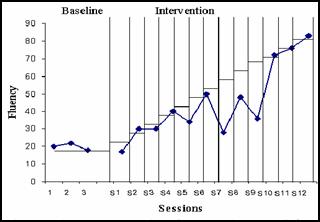
Figure 1. Tracy's fluency as a function of goal setting and reinforcement. Values above horizontal lines indicate Tracy achieved the goal for the session.
The Rasch model is widely used for test development and item functioning. Noisy individuals are often a major concern because they distort item estimates, weakening inferences based on item difficulties. A typical practice is to omit and disregard individuals who are not constructive for item calibration purposes. But application of the Rasch model and information from misfitting participants can assist the evaluation of interventions in research on individuals. By examining misfitting participants useful information can be extracted regarding the strengths and weaknesses of an intervention or the specific behaviors of the individuals involved.
 Figure 1. Tracy's fluency as a function of goal setting and reinforcement. Values above horizontal lines indicate Tracy achieved the goal for the session. |
Figure 1 shows data from Tracy who was subjected to a "goal setting and reinforcement" intervention in order to improve her fluency. Using a changing criterion design, Tracy was asked to reach one goal after another and was reinforced contingently on her performance. The difficulty of the material was increased over sessions. As shown in Figure 1, Tracy reached some of the goals and missed some other, suggesting that the proposed intervention was not all that effective for her.
Using 5 students for comparative purposes I fit a Rasch model to the data of the 6 students by coding student's behavior during a session as 1 (if a student met the goal for that session) or 0 (if the student missed the goal). Given that difficulty increased in every session we can hypothesize that student's behavior could fit the Rasch model (e.g., 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0) for this particular research design. The presence of large fit statistics would suggest a pattern of responding that deviates from the Rasch model, or, in other words, that the intervention has not been as effective as hypothesized. An exception would be a one category responding (e.g., all 1s) which would still indicate that the student behaved contrary to expectations (as if the activity was too easy for the student).
Table 1 shows out-fit mean-square and point-measure correlations for all students, suggesting that Tracy's responding was not in accord to expectations, in comparison to her peers (see also Figure 2).
| Raw Score | Measure | Outfit Mean-square |
Point-measure correlation |
Student |
| 9 8 8 6 6 6 |
1.30 0.83 0.83 0.02 0.02 0.02 |
1.54 0.60 0.88 0.68 0.89 1.58 |
0.12 0.67 0.39 0.68 0.51 -0.07 |
John Lex Bill Mike Steve Tracy |
Table 1. Evaluation of students' response patterns.
Tracy's response pattern, 010101000111, is erratic, but provides useful information regarding her capabilities and her unique reaction to the intervention. She was able to reach some of the most challenging goals, but missed goals of medium and easy difficulty. She may fit the profile of an overachiever who got bored during some of the sessions or a student with attention problems, low motivation, etc. Alternatively, the intervention can be evaluated by examining, refining, and developing the content of the sessions in which Tracy failed, if there is room to improve the content of the test.
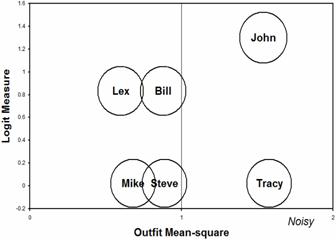 Figure 2. Erratic performance by Tracy and John. |
By focusing on a student's noisy performance, researchers in psychology and education may gain greater understanding of both student behaviors and intervention effectiveness. This knowledge base may assist them in developing effective educational interventions and in remediating learning difficulties.
Georgios, D. Sideridis
Department of Psychology, University of Crete
Noisy Responding and Intervention Effectiveness. Sideridis, G.D. … Rasch Measurement Transactions, 2005, 19:2 p. 1013-4
| Forum | Rasch Measurement Forum to discuss any Rasch-related topic |
Go to Top of Page
Go to index of all Rasch Measurement Transactions
AERA members: Join the Rasch Measurement SIG and receive the printed version of RMT
Some back issues of RMT are available as bound volumes
Subscribe to Journal of Applied Measurement
Go to Institute for Objective Measurement Home Page. The Rasch Measurement SIG (AERA) thanks the Institute for Objective Measurement for inviting the publication of Rasch Measurement Transactions on the Institute's website, www.rasch.org.
| Coming Rasch-related Events | |
|---|---|
| Jan. 16 - Feb. 13, 2025, Fri.-Fri. | On-line workshop: Rasch Measurement - Core Topics (E. Smith, Winsteps), www.statistics.com |
| Apr. 8 - Apr. 11, 2026, Wed.-Sat. | National Council for Measurement in Education - Los Angeles, CA, ncme.org/events/2026-annual-meeting |
| Apr. 8 - Apr. 12, 2026, Wed.-Sun. | American Educational Research Association - Los Angeles, CA, www.aera.net/AERA2026 |
| May. 15 - June 12, 2026, Fri.-Fri. | On-line workshop: Rasch Measurement - Core Topics (E. Smith, Winsteps), www.statistics.com |
| June 19 - July 25, 2026, Fri.-Sat. | On-line workshop: Rasch Measurement - Further Topics (E. Smith, Winsteps), www.statistics.com |
The URL of this page is www.rasch.org/rmt/rmt192a.htm
Website: www.rasch.org/rmt/contents.htm