Li and Hong (L&H, 2001) propose a multi-stage model for relating gene expression profiles to phenotypes. It estimates several Rasch measures associated with each tissue-sample ("person") based on its gene ("item") expression ("response") profile. These measures are used to predict the phenotypes (physical characteristics).
Stage 1: Each data-point is the frequency of a gene-indicator in a tissue sample. The frequencies are stratified into ordinal responses. L&H choose 4 strata, so that the ordinal responses become 0,1,2,3. In their examples, there are about 100 genes and 72 tissue-samples.
Stage 2: The genes are segmented into clusters. L&H use the original data-points, but better would be the residuals from a Rasch analysis of the entire dataset.
Stage 3. A Rasch Partial-Credit analysis is performed on each gene-cluster. This constructs a latent unidimensional variable on which each gene and each tissue-sample is located. The measure for each tissue-sample for each gene cluster is estimated. L&H model each gene to have its own rating-scale structure, but they note that their data are somewhat thin for this type of analysis. A Rasch-Andrich (or gene-grouped) model would be more robust.
Stage 4. The cluster-measures for each tissue-sample are regressed on its observed phenotype, producing a set of regression parameters.
Stage 5. The phenotype of a new tissue-sample is predicted based on its gene expression, the clustering of the genes, and the regression parameters. The predicted phenotype is compared with its observed phenotype to evaluate the success of the cluster-Rasch model.
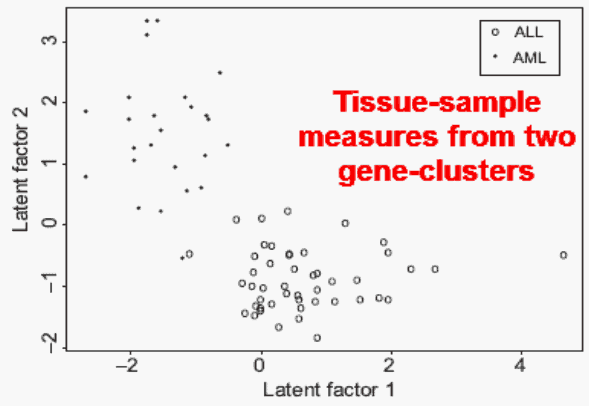
The Figure cross-plots the measures (latent factors) for two groups of tissue-sample and two clusters of genes.
Li H. & Hong F. (2001). Cluster-Rasch models for microarray gene expression data. Genome Biology, 2(8): research0031.1-0031.13

Cluster-Rasch Models … H. Li & F. Hong, Rasch Measurement Transactions, 2008, 22:2 p. 1166
| Forum | Rasch Measurement Forum to discuss any Rasch-related topic |
Go to Top of Page
Go to index of all Rasch Measurement Transactions
AERA members: Join the Rasch Measurement SIG and receive the printed version of RMT
Some back issues of RMT are available as bound volumes
Subscribe to Journal of Applied Measurement
Go to Institute for Objective Measurement Home Page. The Rasch Measurement SIG (AERA) thanks the Institute for Objective Measurement for inviting the publication of Rasch Measurement Transactions on the Institute's website, www.rasch.org.
| Coming Rasch-related Events | |
|---|---|
| Jan. 16 - Feb. 13, 2025, Fri.-Fri. | On-line workshop: Rasch Measurement - Core Topics (E. Smith, Winsteps), www.statistics.com |
| Apr. 8 - Apr. 11, 2026, Wed.-Sat. | National Council for Measurement in Education - Los Angeles, CA, ncme.org/events/2026-annual-meeting |
| Apr. 8 - Apr. 12, 2026, Wed.-Sun. | American Educational Research Association - Los Angeles, CA, www.aera.net/AERA2026 |
| May. 15 - June 12, 2026, Fri.-Fri. | On-line workshop: Rasch Measurement - Core Topics (E. Smith, Winsteps), www.statistics.com |
| June 19 - July 25, 2026, Fri.-Sat. | On-line workshop: Rasch Measurement - Further Topics (E. Smith, Winsteps), www.statistics.com |
The URL of this page is www.rasch.org/rmt/rmt222e.htm
Website: www.rasch.org/rmt/contents.htm