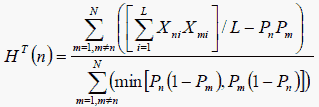
The non-parametric HT fit statistic (Sijtsma, 1986) is a transposed formulation of Loevinger's H scalability coefficient for items. It is evaluated by Karabatsos (2003). He reports "Overall, the HT statistic is best [of 36 person fit statistics] in identifying aberrant test respondents. It is also among the best in detecting each of the five different types of aberrant-responding examinees, and in detecting such examinees in each of the short, medium, and long test conditions."
HT is defined for the rows (persons) of a complete rectangular dichotomous dataset.. Let us focus on person n in a dataset which has L items and N persons. Then, following Karabatsos (2003),
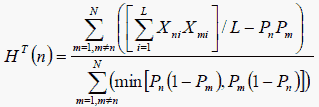
where Xni is the scored (0,1) response of person n to item i, and Pn = Sn/L where Sn is the raw score of person n, and similarly for person m.
HT is the sum of the covariances between person n and the other persons divided by the maximum possible sum of those covariances, so that the range of HT is -1 to +1. When the responses by person n are positively correlated with all the other persons, then HT(n) will be positive. When person n is negatively correlated with all the other persons, then HT(n) will be negative. When personn's responses are random, HT(n) will be close to zero. When the data fit the Rasch model, we expect HT(n) to be somewhat positive, because all the person response strings will correlate positively with the item-easiness hierarchy, and so positively with each other.According to Karabatsos (2003), "the critical values HT = .22 best identify aberrant-responding examinees." In my own informal analyses, the correlation between HT and the Rasch Infit mean-square was about -0.9, but I was unable to identify a unique Infit mean-square value corresponding to HT = .22. Since Sijtsma and Molenaar (2002) report 0.3 to be a critical value for coefficient H, a small simulation study may be required to determine the critical value of HT for a specific empirical dataset.
John Michael Linacre,/p>
Karabatsos, G. (2003). Comparing the aberrant response detection performance of thirty-six person-fit statistics. Applied Measurement in Education, 16(4), 277-298.
Sijtsma, K. (1986). A coefficient of deviant response patterns. Kwantitative Methoden, 7, 131-145.
Sijtsma K,, Molenaar I.W. (2002). Introduction to Nonparametric Item Response Theory. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
A Comment on the HT Person Fit Statistic, J.M. Linacre, Rasch Measurement Transactions, 2012, 26:1, 1358
| Forum | Rasch Measurement Forum to discuss any Rasch-related topic |
Go to Top of Page
Go to index of all Rasch Measurement Transactions
AERA members: Join the Rasch Measurement SIG and receive the printed version of RMT
Some back issues of RMT are available as bound volumes
Subscribe to Journal of Applied Measurement
Go to Institute for Objective Measurement Home Page. The Rasch Measurement SIG (AERA) thanks the Institute for Objective Measurement for inviting the publication of Rasch Measurement Transactions on the Institute's website, www.rasch.org.
| Coming Rasch-related Events | |
|---|---|
| Jan. 16 - Feb. 13, 2025, Fri.-Fri. | On-line workshop: Rasch Measurement - Core Topics (E. Smith, Winsteps), www.statistics.com |
| Apr. 8 - Apr. 11, 2026, Wed.-Sat. | National Council for Measurement in Education - Los Angeles, CA, ncme.org/events/2026-annual-meeting |
| Apr. 8 - Apr. 12, 2026, Wed.-Sun. | American Educational Research Association - Los Angeles, CA, www.aera.net/AERA2026 |
| May. 15 - June 12, 2026, Fri.-Fri. | On-line workshop: Rasch Measurement - Core Topics (E. Smith, Winsteps), www.statistics.com |
| June 19 - July 25, 2026, Fri.-Sat. | On-line workshop: Rasch Measurement - Further Topics (E. Smith, Winsteps), www.statistics.com |
The URL of this page is www.rasch.org/rmt/rmt261f.htm
Website: www.rasch.org/rmt/contents.htm